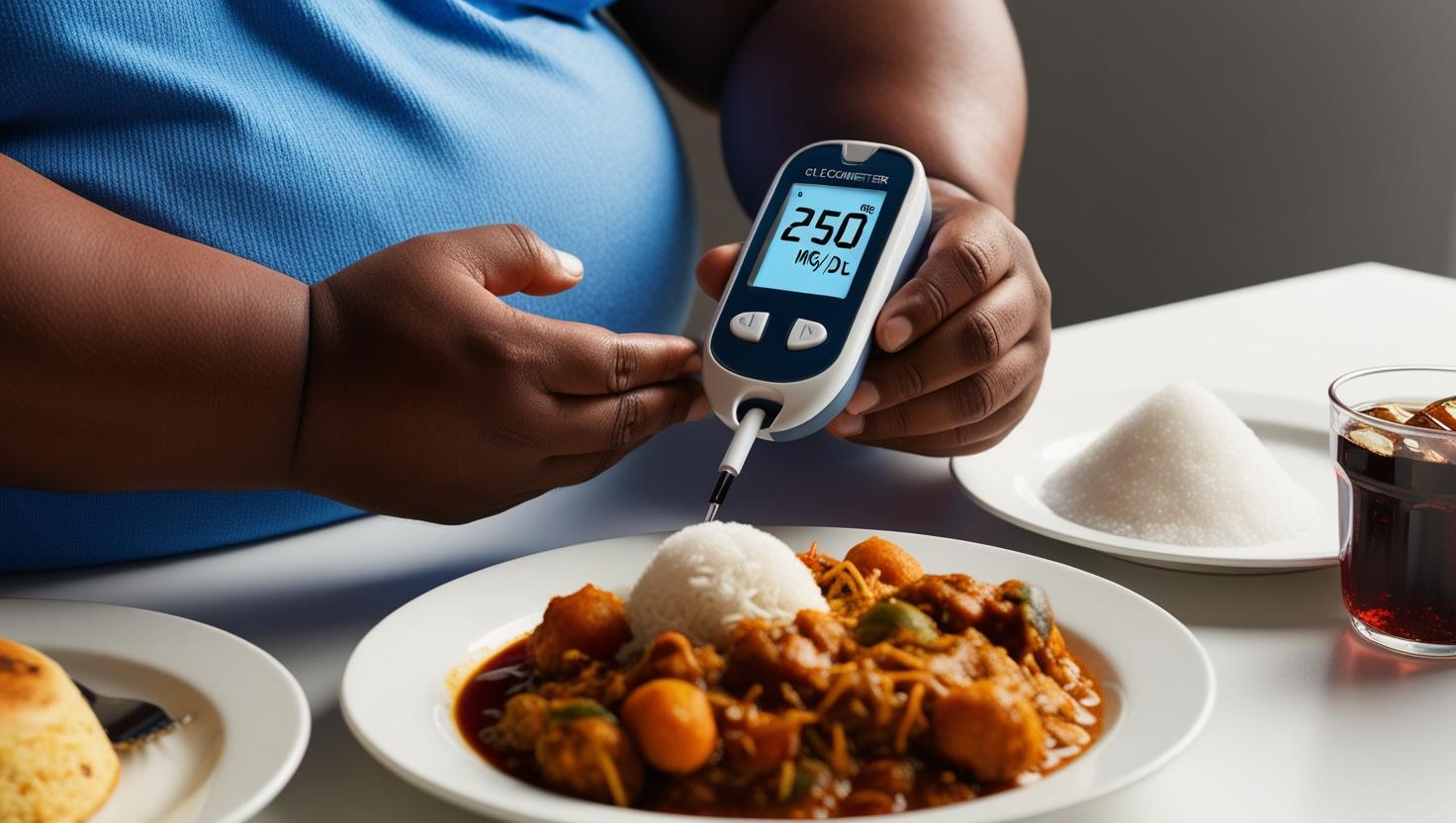
The Sugar Science – Move forward, manage diabetes: Every step counts.
Physical activity plays a major role in managing diabetes and reducing complications. By incorporating physical activity into daily life, individuals with diabetes can enhance insulin action, promoting glucose utilization in cells. Regular physical activity also aids in effective weight management and reduces the risk of complications, such as heart problems and stroke.
A lack of physical activity is a significant risk factor for diabetes, as it contributes to obesity and insulin resistance. Many people lead busy lives, leaving little time for physical activity, and some are unaware of the importance of exercise in maintaining health.
Various types of physical activities are available, including aerobic exercises, yoga, and resistance training. With the guidance of a physician or instructor, you can choose the most suitable physical activity.
Individuals with diabetes must monitor their blood sugar levels before, during, and after physical activity to prevent hypoglycemia. If you’re new to physical activity or unsure about the best exercises for you, consult an experienced physician.
To incorporate physical activity into your daily routine, start with short sessions and gradually increase duration and intensity under expert guidance. Schedule physical activity at the same time each day, just like meals or medication. Engage in enjoyable activities and progress to more intensive training.
Tracking progress with a fitness tracker or mobile app can boost motivation. Physical activity not only helps control blood sugar and prevent complications but also produces serotonin, the “happy hormone,” which enhances mental well-being and reduces stress.
In conclusion, physical activity is essential for individuals with diabetes, alongside diet and medication. By incorporating regular physical activity into daily life, individuals with diabetes can achieve better blood sugar control.